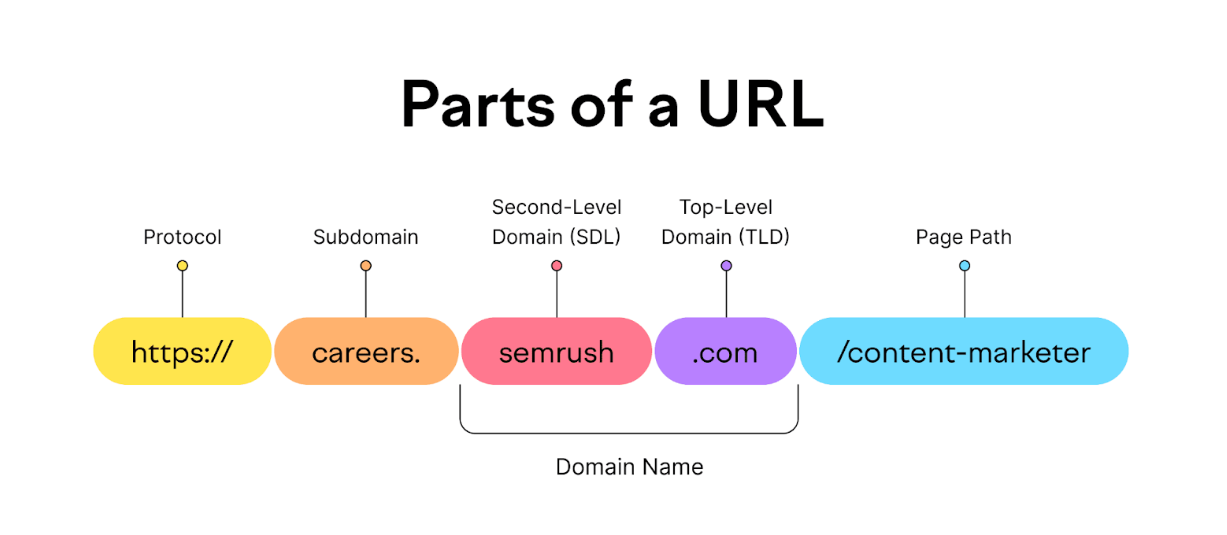
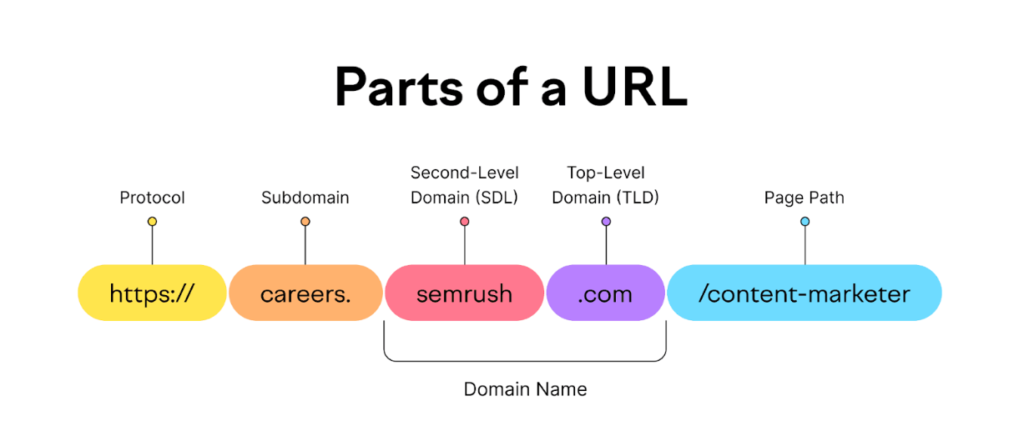
A subdomain is a prefix added to a domain name, creating a distinct part of a website that functions as a separate web address, allowing for organization and separation of content.
Here’s a more detailed explanation:
- Function:Subdomains help organize a website by creating separate sections or areas with their own unique web addresses, like
blog.example.comorshop.example.com. - Structure:A subdomain appears before the main domain name and top-level domain (e.g., “.com”, “.org”) in a URL.
- Examples:
blog.example.com(a blog section)shop.example.com(an online store)support.example.com(a support page)
- Benefits:
- Organization: Subdomains allow you to separate different parts of your website, making it easier to manage and navigate.
- SEO: While not a direct SEO benefit, well-structured subdomains can improve the user experience and potentially lead to better search engine rankings.
- Content separation: Subdomains can be used to host different types of content, such as a blog, an online store, or a community forum.
- Difference from Subdirectories:Subdirectories are folders within a website’s file structure, while subdomains are separate parts of the domain name.
- How to create a subdomain:You typically create a subdomain through your domain registrar or hosting provider.